Herbal pairs are used as a bridge between single herb and polyherbal formulation in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) to supply rationale for sophisticated TCM formulation. The effectiveness and rationality of TCM natural pairs have been extensively utilized as a technique for dietary dietary supplements.
However, as a result of the complexity of the phytochemistry of particular person and mixtures of natural supplies, it’s tough to disclose their efficient and synergistic mechanisms from a molecular or systematic level of view.
In order to handle this query, UPLC-Q-TOF/MS evaluation and System Pharmacology instruments had been utilized to discover the mechanism of motion, utilizing a White Peony (Paeoniae Radix Alba) and Licorice (Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma)-based dietary complement.
A whole of sixteen chemical constituents of White Peony and Licorice had been remoted and recognized, which work together with 73 liver protection-related targets. Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment evaluation had been then carried out together with community evaluation.
Results confirmed that the synergistic mechanism of the White Peony and Licorice natural pair was related to their coregulation of bile secretion and ABC transporter pathways.
In addition, Licorice displays a particular response to drug and xenobiotic metabolism pathways, whereas White Peony responds to Toll–likereceptor signaling, C-type lectin receptor signaling, IL-17 signaling, and TNF signaling pathways, ensuing in the prevention of hepatocyte apoptosis and the discount of immune and inflammation-mediated liver harm.
These findings recommend that a White Peony and Licorice natural pair complement would have a liver-protecting profit via complimentary and synergistic mechanisms. This strategy offers a new path to discover natural compatibility in dietary dietary supplements derived from TCM principle.
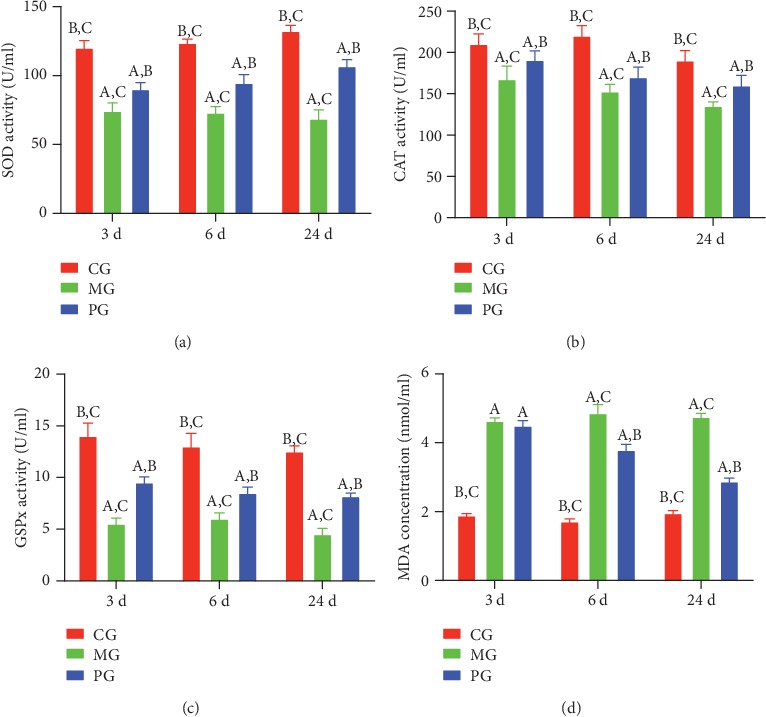
Urinary tract infections are one of the most typical and widespread infectious illnesses. A sure position in etiopathogenesis could play genetic predisposition, in addition to a lower in antiadhesive properties and a rise in urothelium permeability as a result of incompetence of bladder glycosaminoglycan layer.
The prevalence of infectious illnesses will increase considerably with age, in addition to in sufferers with power illnesses.
The introduction of fashionable biotechnology has allowed clinicians to vastly increase therapeutic armamentarium, whereas having a quantity of benefits, together with minimal frequency of issues and adversarial occasions, the risk for long-term use, accessibility, and and so on.
Priority analysis areas embody the research of toll–like receptors, that are transmembrane proteins that present pathogen recognition and activate the immune response.
The position of these receptors in the growth of the immune response to urinary tract infections was evaluated in our research, which permits to foretell the course of the illness and to extend therapy effectivity.
Following preterm delivery, the immature intestine perform and immunology should quickly adapt to deal with bacterial colonization and enteral milk feeding. We hypothesized that intestinal epigenetic adjustments are concerned in the intestine response to preterm delivery and the first feeding.
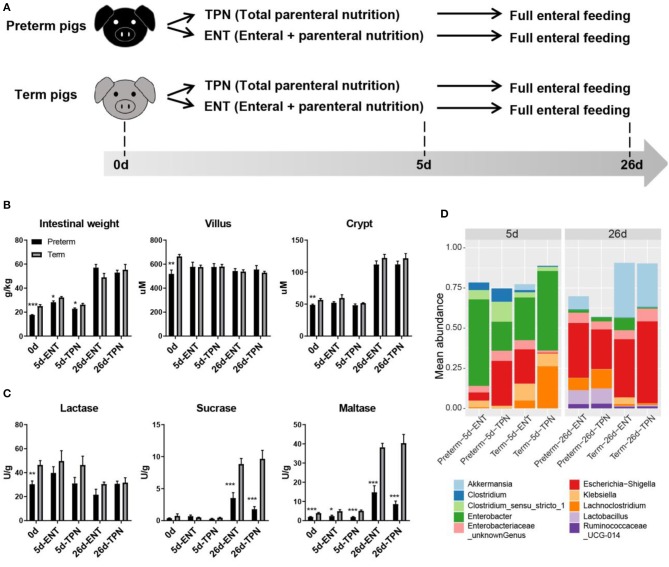
Using piglets as fashions for infants, preterm, and time period pigs had been fed whole parenteral diet (TPN) or partial enteral feeding for five days, adopted by unique enteral feeding with bovine milk till day 26 (weaning age). Intestinal construction, perform, microbiome, DNA methylome, and gene expressions had been in contrast between preterm and time period pigs on days 0, 5, and 26 (n = 8 in every group).
At delivery, the gut of preterm pigs confirmed villus atrophy and world hypermethylation, affecting genes associated to the Wnt signaling pathway. Hypermethylation-associated lowered expression of lipopolysaccharide-binding protein and genes associated to the Toll–likereceptor four pathway had been evident throughout the first 5 days of life, however most early methylation variations disappeared by day 26.
Regardless, sucrase and maltase actions (adult-type brush border enzymes) remained decreased, and the intestine microbiota altered (fewer Akkermansia, extra Lachnoclostridia and Lactobacilli) till day 26 in preterm pigs.
During the 0- to 5-day interval, many new preterm-term methylation variations appeared, however primarily when no enteral feed was offered (TPN feeding). These methylation variations affected intestinal genes associated to cell metabolism, together with elevated GCK (glucokinase) expression by way of promoter hypomethylation.
In conclusion, the immature gut has a outstanding capability to adapt its gene methylation and expression after preterm delivery, and solely few preterm-related defects continued till weaning. Early enteral feeding could also be necessary to stimulate the methylation reprogramming of intestinal genes, permitting fast intestinal adaptation to preterm delivery.